Carbon Removal
Carbon Removal
Companies and societies are well aware that decarbonising and reducing carbon intensities is critical to a healthy, sustainable planet. However, it is not that simple: whilst reductions are imperative, there is no viable pathway through which we can completely eliminate emissions. As a result, carbon removal will become increasingly pivotal in the fight for our future.
Biochar is the most heavily researched, cost-effective Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) method available today. As climate change intensifies, durable carbon removal has never been more urgent- and biochar stands at the forefront of scalable, long-term climate solutions.
Biochar = CDR
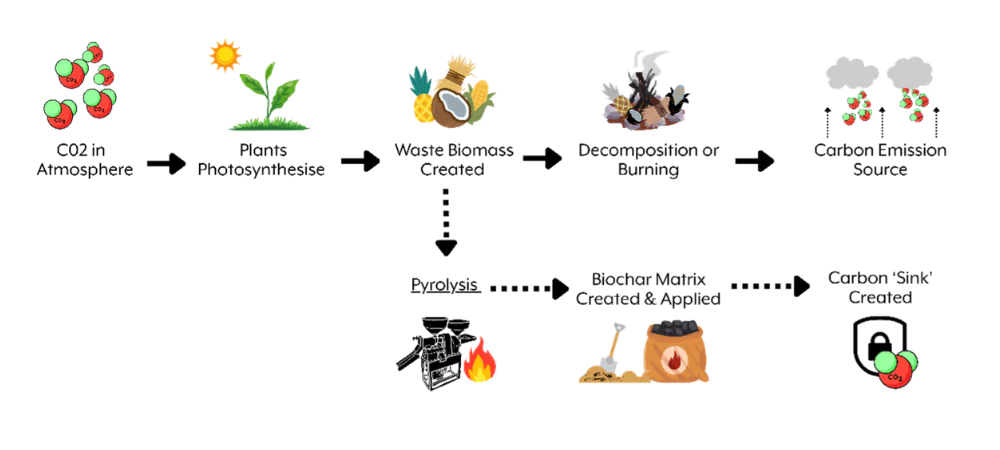
When biomass is heated to high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment (a process called pyrolysis), the charcoal-like solid material remaining is a form of pure, stable carbon. The thermal process locks in the carbon originally absorbed by plants from the atmosphere, preventing it from being released back through decomposition or burning.
When applied to soil or stored in a secure matrix, biochar can sequester carbon for hundreds to thousands of years: far longer than most other nature-based solutions, at a cost much lower than other engineered carbon removal methods. Whilst nuances of biochar’s agronomic benefits are disputed, there is considerable consensus amongst scientists across regions that biochar is a safe, reliable, readily-scalable CDR solution right now.
All Biochar Removes Carbon; But Some Chars are Better than Others
Properly made biochar prevents CO₂ emissions by halting the natural decomposition of organic matter. However, not all biochar is equal in carbon impact.
Key factors affecting carbon removal:
- Feedstock type
- Production method & temperature
- Use case (e.g. soil amendment vs. building material)
High-quality biochar projects use waste biomass, avoid methane emissions, and follow rigorous MRV standards. These projects deliver more verifiable, additional, and permanent carbon removal- and are increasingly prioritised by the market.

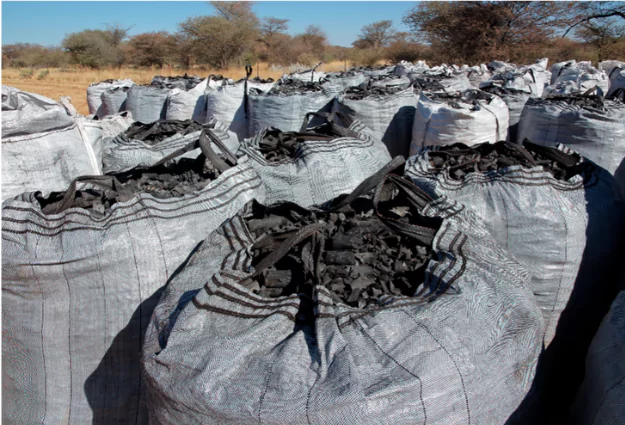
Artisanal vs. Industrial Biochar: Two Models, One Mission
Both artisanal and industrial biochar play vital roles in climate solutions, offering different strengths.
Artisanal Biochar
- Produced with low-tech kilns
- Uses locally available waste biomass
- Promotes rural development, soil health, and community resilience
- Challenges: variable quality, lower MRV reliability, risk of methane emissions if not properly managed
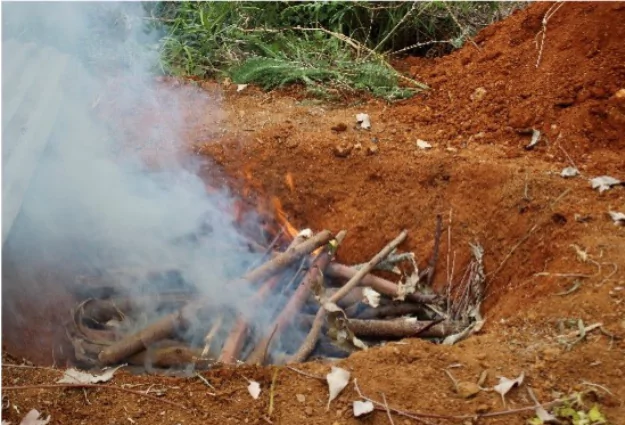
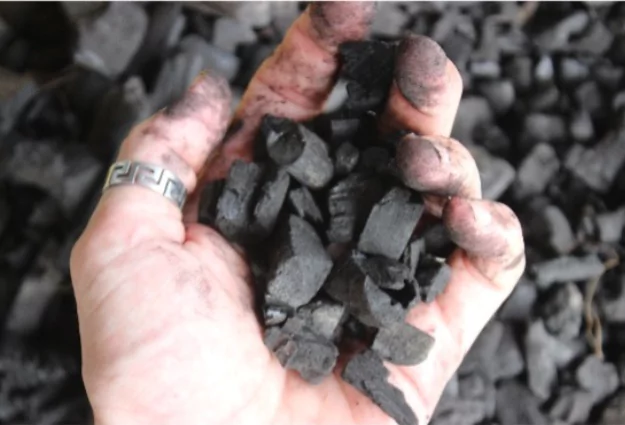



Industrial Biochar
- Produced with high-tech pyrolysis units and emission controls
- Highly consistent quality with certified MRV protocols
- Can deliver large-scale carbon removal
- Challenges: high capital cost and infrastructure/engineering requirements



Bottom line
Artisan biochar offers powerful co-benefits for development and soil regeneration;
Industrial biochar provides scalable, reliable climate impact.
At SBB, we believe both approaches are needed to deliver as much biochar-based carbon removal as possible.
The Science is Clear.
Biochar is pure carbon. Storing it in a stable matrix like soil ensures that carbon stays locked away for good. It is:
- Scientifically-grounded
- Low risk
- Cost-effective
- Ready to scale
- Permanently impactful
Biochar is no longer an emerging solution: it is the most well-understood, immediately deployable method of durable carbon removal available anywhere in the world.
Whether you’re a farmer, processing factory or corporate buyer, biochar is a tool you can trust to meet your climate goals.